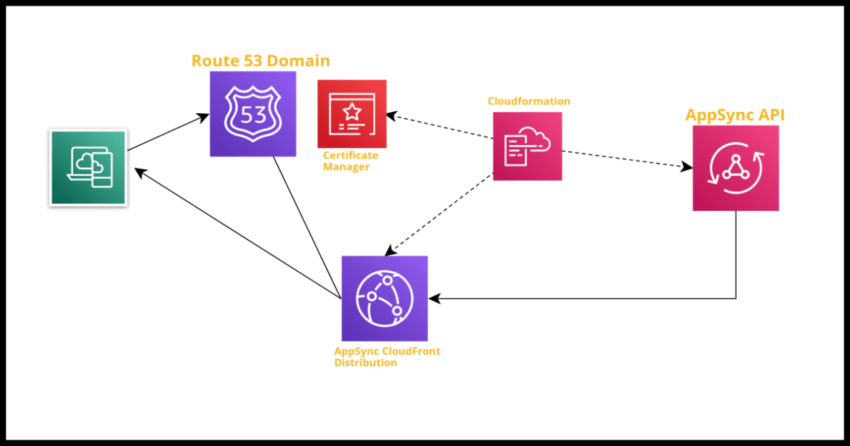
AWS recently updated the support for creating a custom domain name for an AWS AppSync API.
This means you can replace your AWS AppSync Endpoint which is of the form:
{generated-string}.appsync-api.{aws-region}.amazonaws.com/graphql
to something like
{your-api-subdomain}.{your-own-domain-name}.com/graphql
{your-api-subdomain}.{your-own-domain-name}/graphql/realtime (for the websocket endpoint)
Note: This does require you to have an AWS managed certificate for your domain through Amazon Certificate Manager. If you use Route 53 as the registrar for your domains, you should already have one.
This can be done via the AppSync console easily of course – but this post will demonstrate how this can be done just as easily with cloudformation, and save you the bother of redoing this manually if you are replicating your stack.
Explaining the process of creating a custom AppSync domain name
When you initiate a request to create an AppSync custom domain, you will need to provide an AWS Certificate associated with that domain – AppSync will use this to go ahead and create a CloudFront distribution.
CloudFront being global – this created domain name cannot be reused in other regions or accounts.
At this point, there will simply be a CloudFront distribution – with a {generated-name}.cloudfront.net url, but it is not associated with any AppSync API yet.
To associate an API, provide the API ID you want associated with the domain – and AppSync will create an association.
At this point, you will now have your custom domain name configured against the AppSync endpoint, however before you can use it, you will need to add a DNS CNAME record for {your-api-subdomain}.{your-own-domain-name} to route traffic to {generated-name}.cloudfront.net – the CloudFront distro that was created in the first step.
Then we are all set to begin using {your-api-subdomain}.{your-own-domain-name}.com/graphql
Creating an AppSync DomainName and DomainNameApiAssociation in Cloudformation
This is done like below – pass the appropriate values for your own account into the template as parameters.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion: '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Description: appsync custom domain setup template
Parameters:
AWSCertificateARN:
Type: String
CustomDomainName:
Type: String
YourAppSyncApiId:
Type: String
Resources:
AppSyncDomain:
Type: AWS::AppSync::DomainName
Properties:
CertificateArn:
Ref: AWSCertificateARN
Description: Custom domain name using AWS Cert. Example api.your-domain.com
DomainName:
Ref: CustomDomainName
AppSyncDomainAssociation:
Type: AWS::AppSync::DomainNameApiAssociation
DependsOn:
- AppSyncDomain
Properties:
ApiId:
Ref: YourAppSyncApiId
DomainName:
Ref: CustomDomainNameUpdating the DNS records to route traffic to the Cloudfront distribution url
Apologies if you were expecting to see a Cloudformation Template for Route 53 at this step – perhaps at some other point – that deserves an article on its own.
However, the header here is to simply remind the final step which is to add a new CNAME record to the {subdomain}.{your-domain-name}.com that points to {generated-name}.cloudfront.net.
And you should be good to start using the new URL in your applications.